Classes
Spiramycin is a macrolide antibiotic.
DAE Class; Rx
Common Brand Names; ROVAMYCIN FORTE, ROVAMYCIN
Description
Spiramycin is antibiotic and is used to treat a large variety of bacterial infections, such as respiratory tract infections, middle ear infections, skin infections and urinary tract infections. Antibiotics require constant drug level in body for therapeutic effect. This is achieved by taking the drug at regular intervals of time throughout the day and night as prescribed.
It is important to take the drug for the full time period as prescribed, discontinuation of the drug may result in ineffective treatment.
Spiramycin Uses
Spiramycin is primarily used in conditions like Depression, Menopausal symptoms, Nerve weakness, and can also be given in adjunctive therapy as an alternative drug of choice in Fibromyalgia.
Contraindications
Spiramycin is contraindicated in conditions like Hypersensitivity to any component of product.
Sipramycin Side Effects
The severe or irreversible side effects of Spiramycin, which give rise to further complications include Angioedema, Urticaria, Paresthesia, Colitis.
It produces potentially life-threatening effects which include Neuromuscular blockage, Ventricular arrhythmias. which are responsible for the discontinuation of Spiramycin therapy.
The signs and symptoms that are produced after the acute overdosage of Spiramycin include Abdominal pain, Arrhythmias, Headache, Nausea & vomiting.
The symptomatic adverse reactions produced by this drug are more or less tolerable and if they become severe, they can be treated symptomatically, these include Diarrhea, Anaphylactic shock.
Warnings
Antibiotic-associated colitis has been reported with use of spiramycin. Observe for superinfections. Rare hepatic impairment with or without jaundice has occurred with macrolides, it may be accompanied by malaise, nausea, vomiting, abdominal colic, and fever, discontinue use if these occur.
Drug should not be given to Pregnant Mothers, Geriatrics, and Neonates.
Pregnancy and Lactation
Drug should not be given to Pregnant Mothers, and Neonates.
Maximum Dosage
For oral dosage forms (capsules or tablets):
- For treatment of infections:
- Adults and teenagers—1 to 2 grams (3,000,000 to 6,000,000 International Units [IU]) two times a day, or 500 mg to 1 gram (1,500,000 to 3,000,000 IU) three times a day. For severe infections, the dose is 2 to 2.5 grams (6,000,000 to 7,500,000 IU) two times a day.
- Children weighing 20 kilograms (kg) (44 pounds) or more—Dose is based on body weight. The usual dose is 25 mg (75,000 IU) per kg (11.4 mg per pound) of body weight two times a day, or 17 mg (51,000 IU) per kg (7.7 mg per pound) of body weight three times a day.
For injection dosage form:
- For treatment of infections:
- Adults and teenagers—500 mg (1,500,000 IU) injected slowly into a vein every eight hours. For severe infections, the dose is 1 gram (3,000,000 IU) injected slowly into a vein every eight hours.
- Children—Use and dose must be determined by your doctor.
For rectal dosage form (suppository):
- For treatment of infections:
- Adults and children 12 years of age and over—Two or three 750 mg (1,950,000 IU) suppositories per day.
- Children up to 12 years of age—Two or three 500 mg (1,300,000 IU) suppositories per day.
- Newborns—Dose is based on body weight. The usual dose is one 250 mg (650,000 IU) suppository per 5 kg (250 mg suppository per 11 pounds) of body weight once a day.
Missed Dose
If you miss a dose of this medicine, take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular dosing schedule. Do not double doses of any medicine.
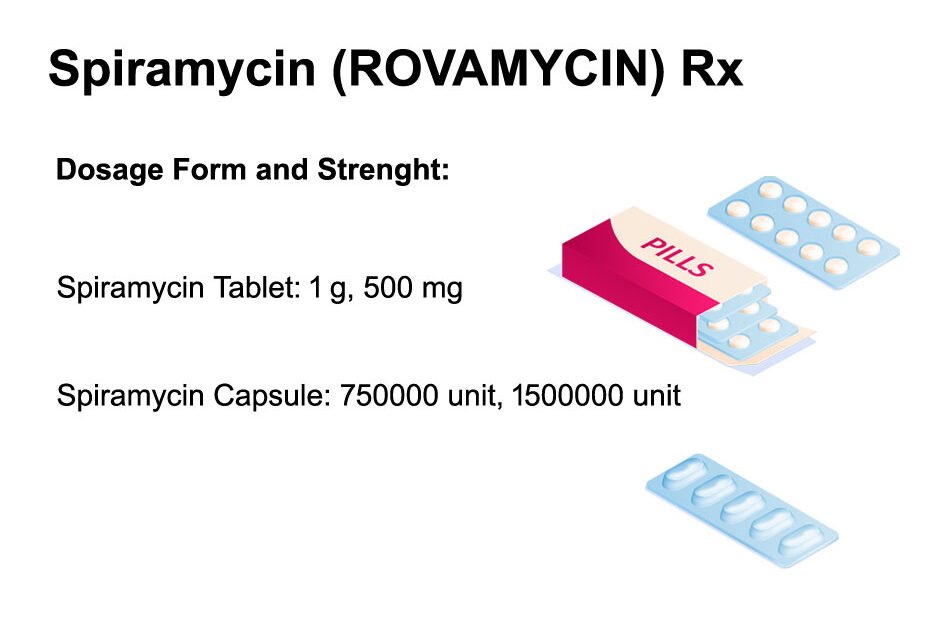
How supplied
Spiramycin dosage form and strenght.
Tablet: 1 g, 500 mg
Capsule: 750000 unit, 1500000 unit