Classes
Roxithromycin is a macrolide with antibacterial properties similar to that of Erythromycin.
DAE Class; Rx
Common Brand Names; RULID, ACTIROX, Forilin, Surlid
Description
Roxithromycin is a macrolide with antibacterial properties similar to that of Erythromycin. It is active against gram positive bacteria for example, staphylococci, streptococci, listeria, corynebacteria; gram negative bacteria for example gonococci, Hemophilus influenza, Hemophilus ducreyi, Legionella, and atypical pathogen, for example mycoplasma and chlamydia. Roxithromycin is well torelated by children and adults. Antibiotics require constant drug level in body for therapeutic effect. This is achieved by taking the drug at regular interval of time throughout the day and night as prescribed. It is important to take the drug for the full time period as prescribed, discontinuation of the drug may result in ineffective treatment.
Roxithromycin Uses
Roxithromycin is primarily used in conditions like Ent infections, Genitourinary tract infections, Pneumonia, Skin infections.
Upper respiratory tract infection: acute pharyngitis, tonsilitis and sinusiti.
Lower respiratory tract infection: acute bronchitis and acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis; community acquired pneumonia. Skin and skin structure infections.
Dental infections
Nongonococcal urethritis.
Skin and skin structure infections
Contraindications
Roxithromycin is contraindicated in conditions like Hepatic disease, Hypersensitivity.
- known hypersensitivity to macrolides, including erythromycin
- severely impaired hepatic function
- concomitant therapy with vasoconstrictive ergot alkaloids
Roxithromycin Side Effects
The symptomatic side effects produced by Roxithromycin are more or less tolerable and if they become severe, they can be treated symptomatically, these include Weakness, Dizziness, Headache, Diarrhea, Rashes, Nausea and vomiting, Elevated alkaline phosphatase, Epigastric pain, GI disturbance, Elevated SGPT & SGOT.
Warnings
Precaution should be taken in hepatic insufficiency, prenancy and lactation. It should be used with caution in patients with any allergy, especially to antibiotics. Take appropriate measures if secondary infection occurs.
Drug should not be given to patients suffering from Kidney dysfunction.
Use in the elderly: No dosage adjustment is required in elderly patients.
Pregnancy and Lactation
Pregnancy (Category B1): The safety of roxithromycin for the human fetus has not been established
Use in lactation: Small amounts of roxithromycin are excreted in the breast milk. Breastfeeding or treatment of the mother should be discontinued as necessary.
Maximum Dosage
Oral
Acute bronchitis, Acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, Acute pharyngitis, Community-acquired pneumonia, Nongonococcal urethritis, Sinusitis, Skin and soft tissue infections, Tonsillitis
One 150 mg tablet morning and evening.
The usual duration of treatment is five to ten days depending on the indication and clinical response.
Streptococcal throat infections require ten days of therapy. The duration of treatment should not exceed ten days.
or two tablets once daily.
or two tablets once daily.
How supplied
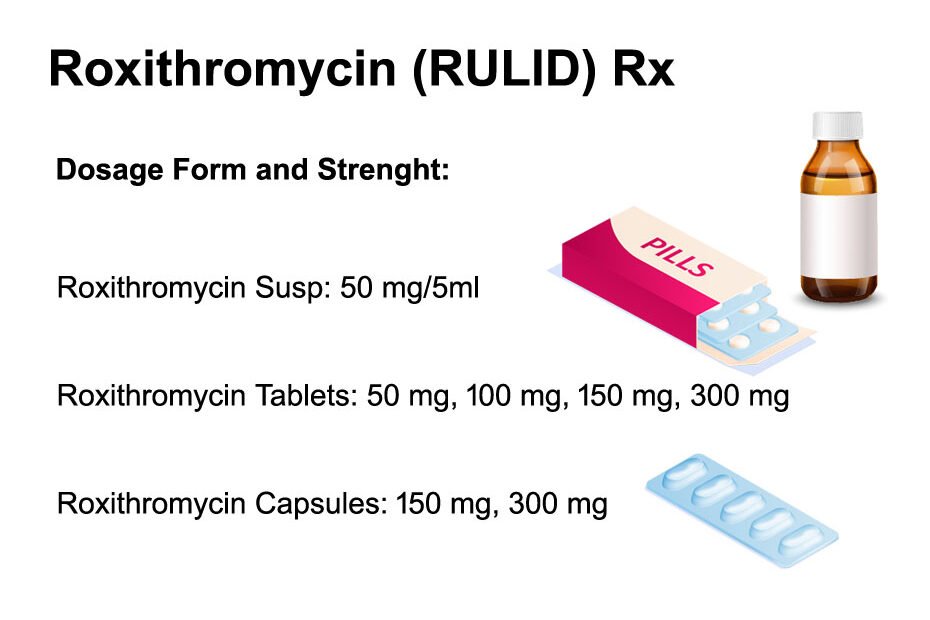
Roxithromycin dosage form and strenght
Suspension: 50 mg/5ml,
Tablets: 50 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg,
Capsules: 150 mg, 300 mg,