This KAPS Quiz contains older questions to help you practise. These questions are no longer used, but they’ll help you understand:
the types of content covered in each paper of the exam how questions might be presented If you want to practise the sample papers under exam conditions, you’ll need to answer all 100 questions in each paper in 2 hours.
KAPS Exam scoring You must complete all questions in the paper or papers you sit.
To pass the exam, you need a mark of at least 50% in all subsections of the exam.
Paper 1 Pharmaceutical chemistry 50% Paper 2 Pharmaceutics 50%
Here is the Test 2 Paper 1 Section 1 = 30 Questions
Section 2 = 70 Questions
Section 1
Trimeprazine belongs to the group of drugs known as:
Alkylamine antihistamines
Phenothiazine antihistamines
Piperidine antihistamines
Monoethanolamine antihistamines
Techniques involving polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can be used to identify all of
the following EXCEPT
Virus types
Actual DNA sequence
Mutations
Bacterial strains
Presence of expressed RNA
The antibacterial action of a sulphonamide, resulting from its blocking bacterial uptake of p-amino-benzoic acid (PABA) is due to the presence of
A nitrogen containing heterocyclic ring
An ionisable acidic proton
A primary aromatic amino group
A sulfonyl urea substituent
To have useful antibacterial activity, a sulphonamide molecule must possess or be
capable of conversion in the body into which ONE of the following?
An alkylated aromatic amino group
An alkoxy group
A chloride group
A non-substituted aromatic amino group
A free sulphonic group
When dimercaprol (B.A.L.) is used to treat heavy metal poisoning, its effectiveness is due to the chelate formed being all the following EXCEPT:
Water soluble
Having a large stability constant
Readily excreted
Non-toxic
Readily metabolised
The chemical bond connecting amino acids in the primary structure of proteins is
A double bond
Hydrolytic in nature
A peptide bond
Between two carbon atoms
Formed by hydrolysis
Conformational isomerism is described as
A form of optical isomerism
Cis-trans isomerism
Possession of a plane of symmetry so that the (+) and (-) rotation around two asymmetric centres is equal and opposite with a resultant cancellation of optical rotatory properties
The non-identical spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule, resulting from rotation about one or more single bonds
The concept that the similarities in physicochemical properties of atoms, groups, radicals and molecules arise from similar electronic structures
Which substance yields the largest number of joules per gram?
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Minerals
Fats
Nucleic acids
The term which describes the time required for the radioactivity of any given amount of a drug to be reduced by 50 percent is:
LD 50
Half-life
Revalue
Retention time
Decay value
One property that phenytoin, phenobarbitone and rifampicin all have in common is that they
Exhibit nonlinear pharmacokinetics
Are used for the treatment of epilepsy
Are poorly absorbed
Can inhibit hepatic drug metabolism
Can induce hepatic drug metabolism
The gamma radiation from radioactive vitamin B12 comes from the:
Iodine atoms
Cobalt atoms
Hydrogen atom
Carbon atoms
Phosphorus atoms
Temazepam, which has the structure below, would MOST probably undergo:
I only
III only
I and II only
II and III only
I and III
I. direct conjugation with glucuronic acid
II. deesterification
III. N-dealkylation
Show hint
Which of the following is TRUE for the hypnotic drug temazepam?
This benzodiazepine has a long half-life and thus induces sleep slowly
The drug is conjugated in the liver and the drug has a relatively short half-life
Intravenous temazepam is an anaesthetic
The drug is metabolised to active compounds which have shorter half-lives than the parent drug temazepam
Temazepam is not as effective a hypnotic as diazepam
The various penicillins that are available differ chemically
In the nature of the acyl side chain
In substituents on the fused ring nucleus
In spatial arrangements of atoms around an asymmetric carbon
In the nature of the original (naturally occurring) nucleus
Only by being different salts
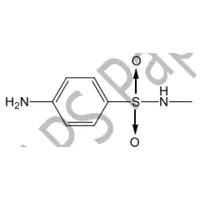
The chemical class of the compound Below is
Sulphonamide
Barbiturate
Phenothiazine derivative
Amine salt
Steroid
Which one of the following acids is polyunsaturated?
Oleic
Glutamic
Palmitic
Linolenic
Stearic
Conformation of organic molecules is MOST commonly determined by which ONE of the following analytical methods?
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
Optical rotation
pK determinations
Biological assay
Mass spectrometry
Oleic acid exists in the cis form. This means:
There also exists an optical isomer of oleic acid
The groups of atoms are formed with double bonds such that there is no rotation and the groups remain on the same side of the molecule
A mirror image of the oleic acid molecule exists
Two groups of atoms are spatially fixed around a double bond so that they are on opposite sides of the molecule
The double bond is part of the ring system
May be dissolved in water by the addition of a small amount of sulphuric acid to convert it to the more soluble bisulphate
Has a sweet, pleasant taste
Does not cross the placenta
Is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract
Is not affected by light
Which of the following compounds contains either an aldehydic or a ketonic functional group?
Methadone
Bentonite
Ephedrine
Glycerol
Amitriptyline
Lignocaine HCl can be infused intravenously and remain stable for long enough to have a therapeutic effect because it
Is an ester
Is an acidic drug
Is an amide
Forms an emulsion in the blood
Can exchange chlorides with sodium chloride
Sodium lauryl sulfate is incompatible with
Cetomacrogo
Sodium stearate
Cetyl alcohol
Polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monostearate
Cetrimide
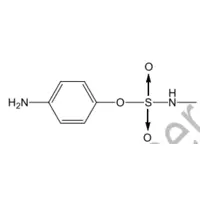
Sulphonamides differ chemically in substitutions that are made on a fundamental structure common to all. That structure is
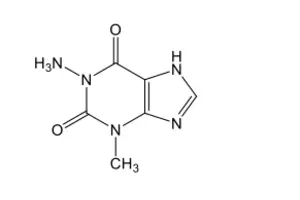
A potential therapeutic use for 1,3-dimethylxanthine is as a(an):
Anxiolytic
Bronchodilator
Hypoglycaemic
Hypouricaemic
Anticoagulant
The metabolism of drugs generally results in
Less acidic compounds
More acidic compounds
Compounds having a higher oil/water partition coefficient
More polar compounds
Compounds with lower aqueous solubility
Which ONE of the following does the chemical structure given above represent?
Aldehyde
Amide
Alcohol
Amine
Carboxyl
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
Conformers can be distinguished by physical methods such as boiling point
Meso-compounds have chiral carbon atoms and are therefore chiral
The D-prefix means the compound rotates plane of polarized light to the right
Cis- and trans-isomers are diastereomers
All compounds which have a carbon atom with four different ligands are chiral
Reagent strips impregnated with glucose oxidase, peroxidase, and orthotolidine are dipped into urine or blood as a test for the presence of glucose.
Glucose is oxidised to CO2, which forms carbonic acid, which turns the orthotolidine a blue colour
Glucose oxidase is reduced to glucose reductase, which converts glucose to a blue colour in the presence of orthotolidine and peroxidase
Glucose is oxidised to gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide; then hydrogen peroxide in the presence of peroxidase converts the orthotolidine to a blue substance
Sucrose is oxidised by glucose oxidase to glucose, which is oxidised to glucuronic acid by peroxidase and orthotolidine to form a dye
Glucose oxidase and atmospheric oxygen oxidise glucose to aldehyde, which undergoes a Schiff test reaction with orthotolidine and peroxidase to yield coloured compounds
An aqueous solution of the sodium salt of an antibacterial sulphonamide would be
Neutral
Strongly basic
Weakly acidic
Weakly basic
Strongly acidic
Glimepiride exerts its hypoglycaemic action by
Causing a direct uptake of glucose by muscle cells
Increasing the metabolism of glucose
Stimulating insulin release from the pancreas
Causing catalytic breakdown of glucose
Blocking the direct uptake of glucose by muscle cells
The KAPS (Knowledge Assessment of Pharmaceutical Sciences) Exam Tests 2 Paper 1 Section 1
Result
Paper 2 Section 1 Pharmaceutical Chemistry Passing Score 50%FAIL
Result
Paper 2 Section 1 Pharmaceutical Chemistry Passing Score 50%PASS
Section 2 Section 1 Completed Section 2
The therapeutic action of allopurinol in gout is due to its effect of
Increasing uric acid excretion
Stimulating purine breakdown
Non-competitively inhibiting xanthine oxidase
Decreasing hypoxanthine levels
Inhibiting adenosine deaminase
Which of the following is LEAST likely to exacerbate seizures?
Alcohol
Sleep deprivation
Cigarette smoking
Psychological stress
Watching television
Is more potent than (-)-hyoscyamine
Is an antidote for anticholinesterase drugs
Is a quaternary amine
May cause constriction of the pupil of the eye
May cause diarrhoea
Which ONE of the following is associated with gingival hyperplasia after long-term treatment?
Irbesartan
Theophylline
Hydrochlorothiazide
Propranolol
Nifedipine
Which ONE of the following statements is CORRECT?
Arteries have thinner smooth muscle layers than veins
Veins generally carry oxygenated blood
Capillary walls have an elastic layer
The pressure inside a vein is less than in an artery
Capillaries provide the greatest resistance to blood flow
All of the following statements about warfarin are correct EXCEPT for:
It resembles vitamin K in structure
It prevents the coagulation of blood in vitro
It has a delay in onset and reversal of action
It prevents synthesis of coagulation factors
Parathyroid hormone has which ONE of the following effects?
Increased mobilization of calcium from bone
Decreased active absorption of calcium from the small intestine
Decreased renal tubular reabsorption of calcium
Decreased resorption of phosphate from bone
Decreased excretion of phosphate
Which ONE of the following is NOT recognized as a central neurotransmitter?
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT)
Noradrenaline
Dopamine
Cyclic adenosine phosphate (cAMP)
Acetylcholine
Levodopa is often the drug of choice in the treatment of parkinsonism. The rationale for the use of this drug is based upon which of the following?
A deficiency of noradrenaline in the subcortical regions of the brain
Dopamine does not readily pass the blood-brain barrier
Tyrosine hydroxylase is a rate-limiting enzyme
Peripheral nerves are deficient in methylating enzyme
Dopamine excess occurs in Parkinson's disease
Is usually the result of blocked sweat glands
Is associated with the growth of Proprionibacterium acnes
Results in scarring where the lesions are occluded
Involves decreased differentiation of epithelial cells
Is not affected by androgen receptor activation
Which of the following is predominately excreted as an unchanged drug
Propoxyphene
Phenytoin
Acamprosate calcium
Codeine
Enalapril
The term "pure opioid antagonist" most appropriately applies to which ONE of the following?
Flumazenil
Tramadol
Hydromorphone
Naloxone
Buprenorphine
The doses of clomiphene citrate, which is used in the treatment of infertility, should be taken on which of the following days of the menstrual cycle?
0-5
5-9
10-14
20-24
24-28
What is the principal way that glyceryl trinitrate relieves the symptoms of angina pectoris?
Slows heart rate
Reduces after-load
Dilates venous capacitance vessels
Constricts arterioles
Dilates major peripheral arteries
Which ONE of the following medicines is an alternative to aminoglycosides for antibiotic prophylaxis in urological surgery?
Ticarcillin
Amoxycillin
Erythromycin
Cefoxitin
Metronidazole
The conjugation of bilirubin occurs mainly in which ONE of the following?
Erythrocyte
Intestine
Liver
Reticuloendothelial system
Kidney
Which ONE of the following statements about dose and response is CORRECT?
Loop diuretics have a dose response curve that reaches a maximum after a few increments of dose
Thiazide diuretics have a steep and prolonged dose response curve
If one drug has greater therapeutic efficacy than another then it is more potent
If one drug is more potent than another drug then it can achieve a therapeutic effect of greater magnitude
The therapeutic index is the maximum tolerated dose divided by the minimum effective dose
Which ONE of the following statements is CORRECT with respect to congestive heart failure (CHF)?
The most common causes of systolic dysfunction in CHF are ischaemic heart disease and hypertension
The primary abnormality in systolic heart failure is an impairment of left ventricular function leading to increased cardiac output
Compensatory responses are beneficial in development and subsequent progression of CHF
ACE-I dose escalation is based on symptomatic improvement
Loop diuretics improve symptoms and survival in CHF patients
The cause of death in acute paracetamol overdose is due to the accumulation of toxic metabolites resulting in:
Hepatic necrosis
Cholestatic jaundice
Acute renal failure
Cirrhosis
Cardiomyopathy
Cyproheptadine can BEST be classified pharmacologically as a(an):
Cholinergic agent
Anti-serotonin agent
Prostaglandin
Anti-prostaglandin agent
Histaminic agent
ß-adrenergic agonists exert an inotropic effect on the myocardium because they:
Increase the conversion of glycogen to glucose
Activate lipases
Promote conversion of phosphorylase "a" to phosphorylase "b"
Decrease the levels of phosphodiesterases
Increase intracellular levels of calcium
Which ONE of the following has the HIGHEST incidence in young women?
Gout
Lupus erythematosus
Ankylosing spondylitis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Osteoarthritis
In regard to urinary tract infections (UTIs) the following statements are true EXCEPT for:
Coagulase negative staphylococci are a common cause of uncomplicated UTIs
The finding of hyaline casts in urine is indicative of a UTI
The most common bacteria in uncomplicated urinary tract infections is E.coli
Onset is usually sudden, typically with frequency, urgency and burning or
painful voiding of small volumes of urine
95 % of urinary tract infections occur when bacteria ascend the urethra to the
bladder
Which ONE of the following is the major determinant of myocardial oxygen
consumption?
Systolic blood pressure
Diastolic blood pressure
Cardiac output
Blood volume
Myocardial fibre tension
Tinnitus, headache, nausea, and sweating are symptoms of which ONE of the
following?
Aspirin hypersensitivity
Paracetamol toxicity
Ibuprofen toxicity
Salicylate toxicity
Paracetamol hypersensitivity
Why is allopurinol used for the treatment of gout?
It increased the renal excretion of uric acid
It inhibits the formation of uric acid
As an anti-inflammatory mechanism
It inhibits prostaglandin synthesis
It alters the sensitivity of pain receptors
Which ONE of the following steroids has markedly different physiological properties to the other four?
Norethisterone
Levonorgestrel
Mestranol
Nandrolone
Megestrol
Of the following agents, the one which possesses the greatest degree of antihistaminic action is
Diazepam
Citalopram
Doxepin
Chlordiazepoxide
Oxazepam
Which ONE of the following is NOT a side effect of amitriptyline?
Blurred vision
Diarrhoea
Dry mouth
Urinary retention
Tachycardia
Which ONE of the following antiepileptic drugs has activity against both generalised tonic-clonic seizures and generalised absence seizures?
Phenytoin
Ethosuximide
Vigabatrin
Valproic acid
Carbamazepine
Mebendazole, a benzimidazole derivative used for the treatment of worm infestations, functions by
Inhibiting worm metabolism
Inhibiting worm reproduction
Weakening the worms to enable ease of flushing by the intestine
Blocking the absorption of nutrients
Paralysis of the worm, detaching them from the host
Which ONE of the following describes a person with normal thyroid function?
Myxoedematous
Basal
Euthyroid
Hypothyroid
Hyperthyroid
The pharmacological effects of sumatriptan arise from its ability to:
Antagonise the actions of serotonin
Mimic the actions of serotonin
Block the effects of dopamine
Constrict inflamed and dilated cranial blood vessels
Which ONE of the following parasites CANNOT infect both animals and man?
Human crab lice (Phthirus pubis)
Dog roundworm (Toxocara canis)
Scabies mite (Sarcoptes scabiei)
Beef tapeworm (Taenia saginata)
Hydatid tapeworm (Echinococcus granulosus)
What is the range for the daily recommended allowance of calcium for women?
300 - 500 mg
500 - 700 mg
700 - 900 mg
1000 - 1500 mg
1500 - 2000 mg
Quetiapine is an atypical antipsychotic similar to clozapine, but unlike clozapine it does have significant antagonist activity at which one of the following receptors?
5-hydroxytryptamine
Dopamine d2
Muscarinic acetylcholine
Histamine H1
Alpha-1 adreno
Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
Ipratropium bromide is of no benefit in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Salmeterol may assist patients with COPD
Ipratopium bromide may cause hyperkalaeamia
Salmeterol may cause hyperkalaemaia
Salmeterol is not likely to affect bone density
Chronic iodine deficiency during adult life results in which ONE of the following conditions?
Cretinism
Myxoedema
Toxic adenoma of the thyroid
Primary thyrotoxicosis
Hyperthyroidism
Which ONE of the following is NOT a feature of psoriasis?
Increased cell turnover
Abnormal scaling
Inflammation
Increased skin thickness
Granulomatous lesions
Plasma t½ is the same at all plasma phenytoin concentrations
Is subject only to first order kinetics
Can increase hepatic drug metabolism
Activity is not affected by kidney function
Symptoms of atropine poisoning include all of the following EXCEPT:
Dry mouth, blurred vision
Tachycardia
Miosis
Hot dry skin
Is a non-steroidal anti-inflammmatory drug administered intramuscularly to control post-surgical pain
Is an anti-depressant with minimal anticholinergic properties
Can be used in patients with active peptic ulcers
Can cause CNS and respiratory depression
Is commonly used in the elderly and young patients with impaired renal
function
Immediate or anaphylactic hypersensitivity:
May occur after prolonged exposure to an antigenic material
Is caused by direct contact with the noxious material
Does not involve antibody production
Involves IgE antibody production
Effects are always generalised and produce anaphylactic shock
Cough receptors are present in which ONE of the following?
Cerebellum
Nasopharynx
Pharynx
Medulla
Epithelial lining of the tracheobronchial tree
Each of the following is a major determinant of myocardial oxygen demand EXCEPT for:
Heart rate
Myocardial contractility
Coronary blood flow
Left ventricular volume
Myocardial wall tension
Dilation of the pupil
Constriction of the pupil
Nearsightedness
Intolerance to light
A blind spot in the vision
In which ONE of the following drugs is the pharmacological activity associated with optical isomers?
Warfarin
Carbamazepine
Heparin
Acetylcholine
Phenytoin
Which one of the following eye drops causes rapid mydriasis and has a duration effect of only 2 to 3 hours?
Physostigmine 0.5%
Homatropine 1%
Timolol 0.5%
Phospholine iodine 0.125%
Adrenaline eye drops 1%
Which ONE of the following statements concerning fats and carbohydrates is MOST appropriate?Fats and carbohydrates:
Differ in that fats contain more oxygen than carbon
Are alike because they contain the same amount of nitrogen
Are both changed into fatty acids during digestion
Are alike because they both release energy in the cells
Are alike because neither can be stored
Is usually the result of a congenital deficiency in α1-antitrypsin
Is characterised by abnormal enlargement of alveoli
Is always accompanied by chronic bronchitis
Is associated with an increase in elastic recoil
Is associated with impaired inspiration rather than expiration
All of the following statements regarding tyramine are true EXCEPT
It is a direct acting sympathomimetic amine
It releases noradrenaline from sympathetic nerve endings
It is potentiated by monoamine oxidase inhibitors
It can cause hypertension in persons treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors
Which type of vitamin is MOST toxic above the tolerable upper limit?
Water soluble
Fat soluble
Vitamin C
Hematopoietic
Energy releasing
Discarding outdated or improperly stored tetracyclines is especially important because they may:
Lose all potency
Become more likely to cause dental pigmentation
Become insoluble and cannot be absorbed
Change into more toxic forms
Develop an unpleasant odour and taste
Two drugs may act on the same tissue or organ through independent receptors, resulting in effects in opposite directions. What is this known as?
Physiologic antagonism
Chemical antagonism
Competitive antagonism
Irreversible antagonism
Dispositional antagonism
Is bound to Na+/K+ATPase in the heart
Potentiates Na+/K+ATPase
Has a prominent effect on the transport of divalent cations
Would be expected to increase the potassium content of the myocardium
All of the following are features of hypoglycaemia EXCEPT for:
Feeling of faintness
Confusion
Disorientation
Sweating
Smell of acetone on breath
Cardiac glycosides increase the force of contraction by
Stimulating the sodium/potassium pump to lower intracellular sodium levels
Inhibiting the sodium/potassium pump, causing secondary rise in calcium accumulation
Inhibiting cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase to increase intracellular cyclic AMP levels
Increasing the removal of calcium from the cell by the sodium-calcium exchange
Cephalosporins typically covers all strains of streptococci EXCEPT for:
Streptococcus viridans
Streptococcus faecalis
Alpha haemolytic
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus milleri
Of the following, which adverse reaction is NOT associated with frusemide?
Hyperuricaria
Tinnitus
Fluid and electrolyte imbalance
Hypotension
Metabolic acidosis
Propranolol could be used in the management of the following conditions EXCEPT for:
Oesophageal varices
Angina pectoris
Cardiac dysrhythmias
Parkinsons disease
Migraine
Following shock, intravenous sodium bicarbonate is used to:
Increase blood flow to poorly perfused tissue
Neutralise lactic acid
Increase plasma pCO2
Depress the increased respiration caused by acidosis
Increase peripheral vasodilation
The intrinsic activity or efficacy of a drug is
A measure of its potency
Related to its maximal agonist effect
Restricted to describing antagonists
The negative logarithm of the concentration producing half the maximum
response
Which ONE of the following is a penicillin which is effective in the presence of
penicillinase?
Amoxycillin
Flucloxacillin
Phenoxymethylpenicillin
Phenethicillin
Ticarcillin
Which ONE of the following is characterized by excess secretion of thyroid hormone?
Addison's disease
Gilbert's syndrome
Grave's disease
Werner's syndrome
Wilson's disease
The pain associated with angina pectoris is caused by which ONE of the following?
Spasm of the aorta
Electrolyte imbalance on the myocardial surface
Ventricular tachycardia
Aortic stenosis
Ischaemia of some area of the myocardium
Simvastatin is effective in lowering:
LDL cholesterol
HDL cholesterol
LDL cholesterol and plasma triglycerides
Plasma triglycerides and HDL cholesterol
LDL cholesterol, plasma triglycerides and HDL cholesterol
Use of the antiarrhythmic prescribed on September 30 is limited because of which ONE of the following side effects?
Aplastic anemia
Anorexia
Thrombocytopenia
Irreversible paresthesia
Exacerbation of arrythmia
Which ONE of the following should be regularly monitored for amiodarone toxicity?
Prostate specific antigen (PSA
Thyroid function tests (TFT
International normalised ration (INR)
Serum creatinine
Urinary cortisol
Mr Piper complains of bilateral shoulder and hip muscle pain. Which ONE of the following tests is MOST appropriate to investigate his symptoms?
Complete blood count
Liver function tests
Thyroid function tests
Electromyogram
Creatine kinase
Which ONE of Mr Piper's medications is MOST likely to be implicated in his muscle pain?
Amiodarone
Simvastatin
Flecainide
Ciprofloxacin
The KAPS (Knowledge Assessment of Pharmaceutical Sciences) Exam Tests 2 Paper 1 Section 2
Result
Paper 2 Section 1 Physiology and Pharmacology Passing Score 50%rnrnFAILrn
Result
Paper 2 Section 1 Physiology and Pharmacology Passing Score 50%rnrnPASSrn
Section 2 Completed Sample Test 1 Sample Test 2 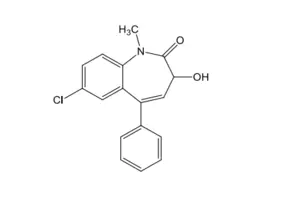 1
1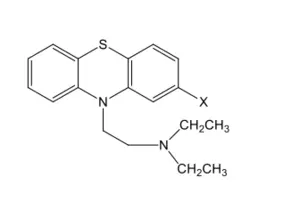 1
1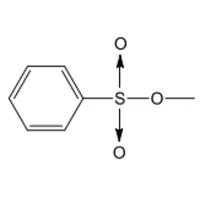

 1
1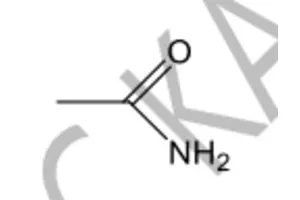 1
1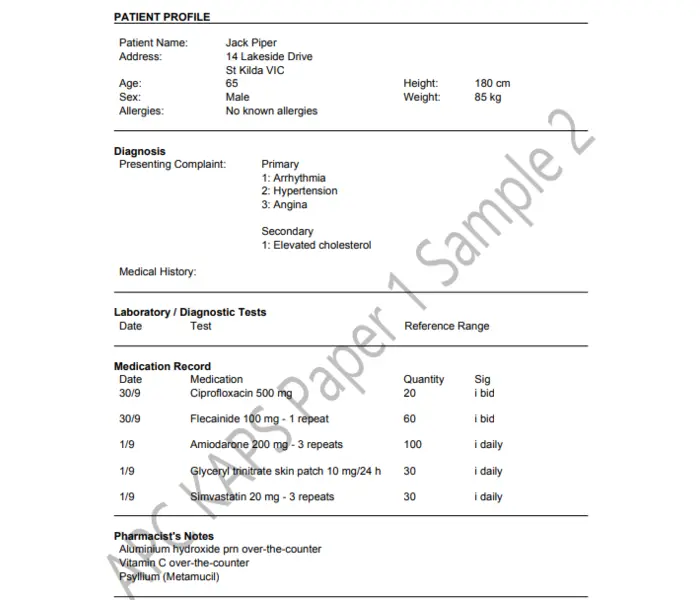 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1
Great job!! Really appreciated.