Classes
Cefpirome is a fourth generation cephalosporin antibiotic.
DAE Class; Rx
Common Brand Names; CEFROM
Description
Cefpirome is a fourth generation cephalosporin antibiotic. Cephalosporins are derivatives of 7-aminocephalosporic acid and are closely related to penicillins in structure. Cephalosporins have a six membered sulfur containing ring adjoining a ß lactam ring. Cefpirome is effective in a large variety of bacterial infections, such as respiratory tract, ear, skin, septicaemia, infections in immunocompromized patients and urinary tract infections. Antibiotics require constant drug level in body for therapeutic effect.This is achieved by taking the medication at regular interval of time throughout the day and night as prescribed. It is important to take the drug for the full time period as prescribed. If you discontinue the therapy, it may result in ineffective treatment.
Cefpirome Uses
Cefpirome is primarily used in conditions like Bacteremia, Lower respiratory tract infections, Pneumonia, Promyelocytic leukemia, Septicaemia, Severe infections including bacteraemia and septicaemia and infections in neutropenic patients, Skin infections, Soft tissue infections, Urinary tract infection.
Contraindications
Cefpirome is contraindicated in conditions like Hypersensitivity.
Cefpirome Side Effects
The side effects of Cefpirome, which give rise to further complications include Thrombocytopenia, Granulocytopenia, Agranulocytosis, Eosinophilia, Hemolytic anemia, Hemolytic anemia, Eelvated hepatic enzymes, Superinfection.
It produces potentially life-threatening effects which include Anaphylaxis. which are responsible for the discontinuation of Cefpirome therapy.
The symptomatic adverse reactions produced by this medicine are more or less tolerable and if they become severe, they can be treated symptomatically, these include Nausea, Vomiting, Abdominal pain, Rashes, Urticaria, Pseudomembranous colitis, Increase in liver enzymes.
Warnings
Cefpirome should be used with caution in patients with impaired kidney or liver function. Appropriate measure should be taken if secondary infection occurs.
As with other beta-Iact a mantibiotic granulocytopenia and, more rarely, agranulocytosis may develop, particularly if it is given over longer periods.The blood cell count should therefore be monitored for courses of treatment lasting far more than 10 days.
Severe and persistent diarrhoea may occur with broad spectrum antibiotics during treatment or in the weeks following discontinuation. These episodes may be symptomatic of pseudomembranous colitis (in most cases, due to Clostridium difficile). This event, which is
rare with cephalosporins, may be life-threatening.
Even if pseudomembranous colitis is only suspected, administration of it must be halted immediately. This type of colitis requires immediate and appropriate treatment by a physician. Drugs that inhibit intestinal motility (peristalsis) must not be taken in such cases. Insufficient clinical experience has been gained with this medicine in children.
Drug should not be given to Pregnant Mothers, patients suffering from Kidney dysfunction, and Neonates.
Pregnancy and Lactation
Drug should not be given to Pregnant Mothers
Maximum Dosage
Adult Dosage
1 to 2 g/12 hourly / IV
Paedriatic Dosage (20kg
–
Neonatal Dosage (3kg)
–
How supplied
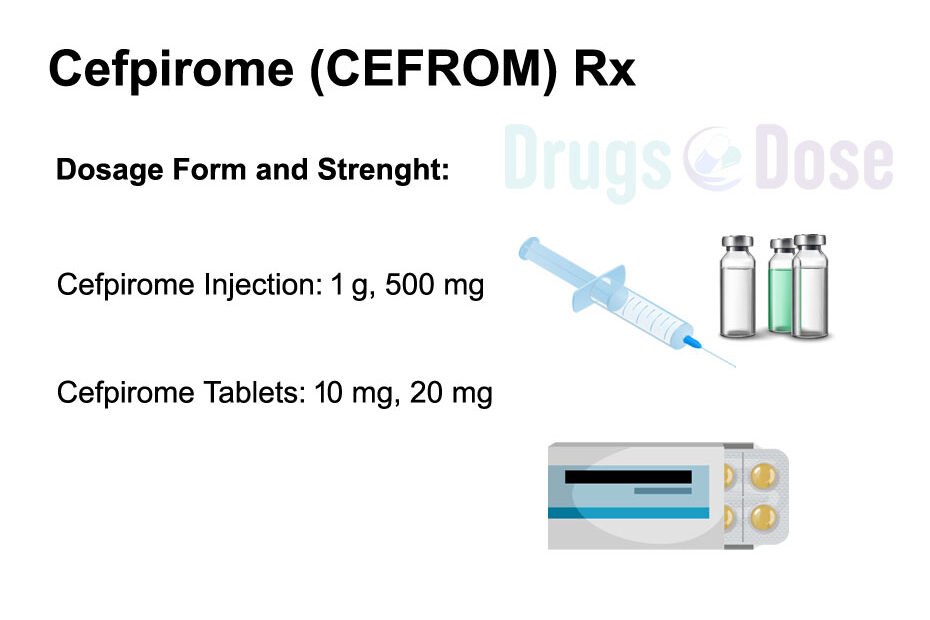
Cefpirome dosage form and strenght
Injection: 1 g, 500 mg
Tablets: 10 mg, 20 mg