Drugs Pediatric Dose Calculator Based on body surface area Catzel Rule
- The Nomogram method or Catzel Rule is utilized to determine the correct pediatric medication dosage based specifically on the patient’s size. The patient’s size is identified as body surface area (BSA) in meters squared (M2). The average adult client (weighing 150 – 154 lbs) will have a BSA of 1.73M2.
The nomogram chart can be used to identify the patient’s BSA based on their height and weight (in. and lbs. or cm and kg).
To Calculate Body Surface Area
Nomogram method: The surface area is determined where a straight line connecting the patient’s height and weight crosses over the BSA column
Example 1:
If the adult dose of a drug is 100 mg, calculate the approximate dose for a child with a BSA of 0.83 m2 ?
Answer
𝐶ℎ𝑖𝑙𝑑 ′𝑠 𝑑𝑜𝑠𝑒 = 0.83𝑚2/ 1.73𝑚2 𝑥 100𝑚𝑔 = 47.97𝑚𝑔 𝑜𝑟 48𝑚g of drug
Example 2:
If the adult dose of a drug is 75 mg, what would be the dose for a child weighing 40 lb. and measuring 32 inch in height using the BSA nomogram?
Answer
First calculate BSA of child based on given weight and height; then convert pounds to kg and inch to centimeter;
- 1kg=2.2Ib; 40 I𝑏 𝑥 Kg/ 2.2Ib=18.18kg; and
- 1 inch=2.54 cm; 32inch 𝑥 2.54cm/ 1inch=81.28cm.
BSA of children =√Weight (kg) × height (cm) /3600=√18.18kg*81.28cm/3600 =√1477.7/3600=√0.4=0.6m2
Child dose=0.6m2 / 1.73m2 × 75mg=0.35*75mg=26mg of medicine
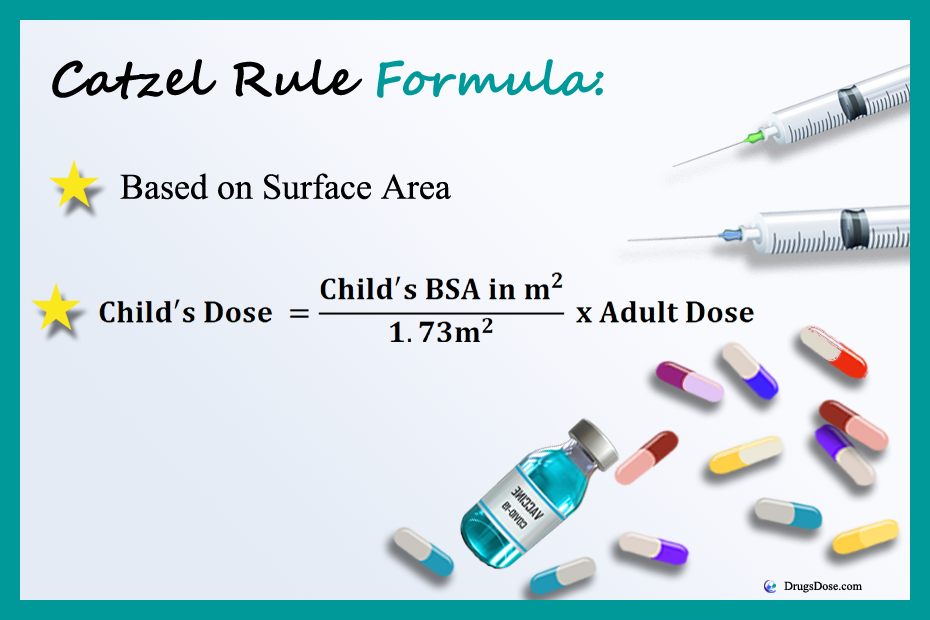
Formula:
Dose for Child = Surface Area of Child / Surface Area of Adult x Adult Dose
To Calculate Body Surface Area
General Tips:
- Check that your answer makes sense clinically.
- Triple check your work.
- Have a colleague or pharmacist check your work.
- Know general therapeutic drug doses for commonly administered medications.