How to Use Body Surface Area Calculator (Mosteller Method)
This review will discuss how to solve nursing dosage and calculations on body surface area!
Body surface area is used to help calculate the most accurate medication dosage for a patient. For example, some medications ordered for a pediatric patient may be based on body surface area (BSA) and strong medications, such as chemo agents (anticancer medications).
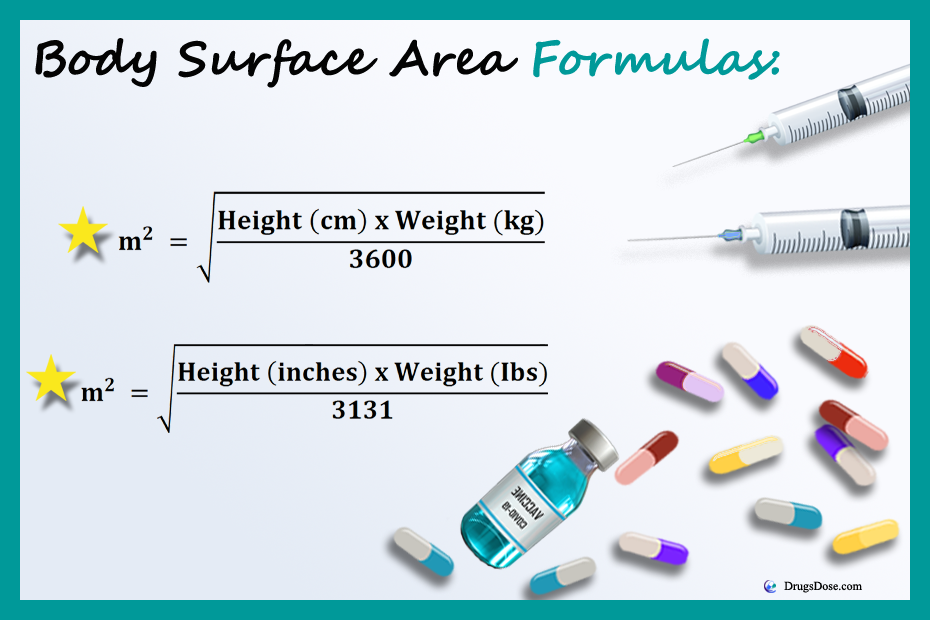
The first two formulas will help you calculate the body surface area and you will select which formula to use based on if the scenario gave you the patient’s weight and height in the Imperial or metric system.
- You will use the FIRST formula below if the weight and height are in kilograms (kg) and centimeters (cm).
- m² = √Weight (kg) × height (cm) /3600
- You will use the SECOND formula below if the weight and height are in pounds (lbs) and inches (in).
- m² = √Weight (Ibs) × height (inches) /3131
Normal values
- “Normal” BSA is generally taken to be 1.7 m².
- Average BSA for men: 1.9 m²
- Average BSA for women: 1.6 m²
- Average BSA for child (9 years): 1.07 m²
- Average BSA for child (10 years): 1.14 m²
- Average BSA for child (12-13 years): 1.33 m²
- Average BSA for neonate: 0.25 m2
- Average BSA for 2 year old child: 0.5 m2
General Tips:
- Check that your answer makes sense clinically.
- Triple check your work.
- Have a colleague or pharmacist check your work.
- Know general therapeutic drug doses for commonly administered medications.